
Curriculum Connection
All You Need to Know
Engineering
Design process used to design and construct the parachute
Technology and engineering design process was applied when constructing the parachute. The design challenge/ problem or STEM Project challenge was to design and build a model of a parachute man that will fly and land safely after being dropped from a height. However, there were constraints faced during the design and construction of the parachute. The criteria were to apply the design process and construct a model that meets the expected results otherwise redesign until expected outcome or result is achieved.
The criteria was to construct a Parachute that is cost effective which means how much of each material will students need to construct a model of a parachute that will land safely?
Technology
Technology/tools used to build the parachute
Technology provides an opportunity for students how to use knowledge, tools and skills in math and science to design and construct the parachute. Students will use tools such as scissors, digital camera to capture the movement of the falling parachute, digital clock to record the time.
Mathematics
Mathematics is used to calculate the cost of the parachute
Calculate surface area, average velocity, acceleration due to gravity
Students will model variables such as type of material, surface area and average speed.
Findings
What is the relationship between the type of material and average speed?
What is the relationship between the surface area and average speed?
What happens to the speed of the parachute if the surface area is increased?
Compare the speed of the parachute for the different types of materials with the
same surface and same distance?
How do we know parachute landed safely?
Modelling the cost of constructing a parachute
Design Challenge
Design a model of a parachute that will land safely and be economical to build.
What design do you think would be the best for this challenge? Sketch your parachute design and brainstorm some ways to construct your parachute at a minimum cost but the parachute must meet the design challenge – it must land safely.
Science
Science is applied for the parachute to fall slowly and for the parachute man to land safely
Explore the concepts of air resistance, type of material used for the parachute, weight force or gravitational force, how surface area affects air resistance, acceleration due to gravity, balance and unbalance forces etc……
Different concepts from STEM disciplines


Science Concepts
Science is applied for the parachute to fall slowly and for the parachute man to land safely
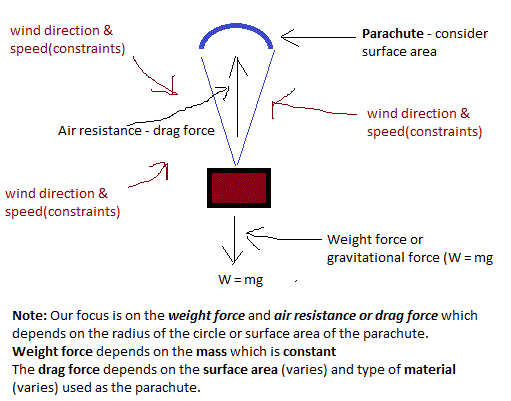
Air resistance or Drag force & Weight Force
Weight force(W) = mg
where m = mass of the parachute man and g is acceleration due to gravity(10m/s2). That means if mass (m) increases, weight force increases. However, mass in our project is kept constant. Mass is an independent variable

Surface Area Against Drag Force
Drag force or air resistance depends on the surface area or radius of material used. Once surface area of material used increases, air resistance or drag force also increases. This also affects the average speed of the parachute once dropped above ground level. The speed of the parachute will decrease once increase surface area.

Drag Force Against Speed
Once air resistance or drag force increase, it reduces the speed of the parachute.
Surface area and type of material used as parachute are dependent variables.
Balance & Unbalance force
Let W = Weight force
Drag force or air resistance = R
If :
W›R = parachute will drop or fall towards ground level with varying speed.
Therefore, increase the drag force or air resistance (by increasing the surface area or radius of the material) to decrease the speed of the falling parachute and the parachute man can land safely
What happens if : W‹R or W⁼R?????
Get in touch for more information.
Mathematics Concepts
Calculate surface area, average velocity, acceleration due to gravity
Students will model variables such as type of material, surface area and average speed & cost of building the parachute.

Criteria & Design Challenge
Parachute should be cost effective. How much of each material will students need to construct a model of a parachute that will land safely?

Calculate the maximize cost
Students will also model the cost of the material taking into consideration that it must be cost effective,same time it must meet the design challenge.
Findings
What is the relationship between the type of material and average speed?
What is the relationship between the surface area and average speed?
What happens to the speed of the parachute if the surface area is increased?
Compare the speed of the parachute for the different types of materials with the same surface and same distance?
How do we know parachute landed safely?

Modelling the cost of constructing a parachute
Design Challenge
Design a model of a parachute that will land safely and be economical to build.
Materials
Note: Some materials have no cost but only some with their costs are shown below.
What design do you think would be the best for this challenge? Sketch your parachute design and brainstorm some ways to construct your parachute at a minimum cost but the parachute must meet the design challenge – it must land safely.
Example
Let a = newspaper, b = aluminium foil, c = nylon rope,
d = sticky tape.
Cost = a + c + d or Cost = b + c + d
Cost = 50a + 10c + 90d or 25b + 10c + 90d
Let d (sticky tape- need only one) be a constant and vary the values of variables a, b & c.
Note: can not combine variables a & b in one design. They must be used in separate designs
Then,
Cost = 50a + 10c + 90 or Cost = 25b + 10c + 90
Example
Cost = 50x2 + 10x6 + 90 or Cost = 25x2 + 10x6 + 90
Cost = 100 + 60 + 90 or Cost = 50 + 60 + 90
Cost =K2.50 or Cost = K2.00
The two costs above is when we use 2 of (10cmx10 cm) of newspaper and aluminium foil respectively and 6 of 20cm long nylon rope for each design.

Calculate the maximize cost
Students will also model the cost of the material taking into consideration that it must be cost effective,same time it must meet the design challenge.
Findings
What is the relationship between the type of material and average speed?
What is the relationship between the surface area and average speed?
What happens to the speed of the parachute if the surface area is increased?
Compare the speed of the parachute for the different types of materials with the same surface and same distance?
How do we know parachute landed safely?
Testing & observations of Parachute designs
This Video highlights testing, observations, and recording of the different parachute designs when drop from a fixed height.
Skydiving
Observe the design and how a parachute is being used for safe landing




